What is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer is a malignant condition that arises when the cells within the breast tissue begin to proliferate uncontrollably, resulting in the formation of tumors. These tumors can be in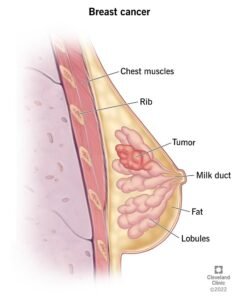 vasive, meaning they spread to nearby tissues, or non-invasive, characterized by their confinement to the original site of development. Understanding the biology of breast cancer is essential, as it aids in recognizing its various forms and implications for treatment. The most common subtype is ductal carcinoma, which originates in the milk ducts, while lobular carcinoma begins in the lobules, where milk is produced. Other types include inflammatory breast cancer and triple-negative breast cancer, each having distinct characteristics and varying prognoses.
vasive, meaning they spread to nearby tissues, or non-invasive, characterized by their confinement to the original site of development. Understanding the biology of breast cancer is essential, as it aids in recognizing its various forms and implications for treatment. The most common subtype is ductal carcinoma, which originates in the milk ducts, while lobular carcinoma begins in the lobules, where milk is produced. Other types include inflammatory breast cancer and triple-negative breast cancer, each having distinct characteristics and varying prognoses.
The etiology of breast cancer is multifaceted, influenced by a mixture of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Certain hereditary mutations, notably in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, dramatically increase the likelihood of developing breast cancer. Additionally, its prevalence varies across demographics, with age and gender being significant risk factors. Women are more likely to develop breast cancer than men, although men can also be diagnosed, albeit at lower rates. Moreover, ethnicity plays a role, as certain groups, such as African American women, tend to have lower survival rates despite a similar incidence rate compared to Caucasian women.
Statistics indicate that breast cancer is one of the most common cancers globally, underscoring the importance of awareness and early detection. Regular mammograms and self-examinations are critical in identifying abnormalities at an early stage, which significantly enhances treatment options and outcomes. The societal impact of breast cancer is profound, prompting ongoing research and advocacy aimed at improving survival rates and quality of life for affected individuals. By understanding what breast cancer is, one can advocate for better prevention strategies and contribute to the fight against this pervasive disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
Breast cancer is a multifaceted disease, influenced by various factors that interact in complex ways. Understanding its causes and risk factors is essential for prevention and informed decision-making. A prominent factor in an individual’s likelihood of developing breast cancer is genetic predisposition. Approximately 15-20% of breast cancer cases are linked to inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. Those with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer should consult genetic counselors to evaluate their risk and consider regular screenings.
Lifestyle choices also play a significant role in the development of breast cancer. Studies indicate that excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and physical inactivity are associated with a higher risk. A diet low in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while high in processed foods may contribute to breast cancer risk. Moreover, tobacco use has been implicated, although its connection to breast cancer is less well-established compared to other forms of cancer.
Environmental factors also contribute to the risk profile of Breast Cancer. Exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants, such as those found in industrial work environments, has been investigated for potential links. Additionally, prolonged exposure to radiation, particularly during medical treatments, can elevate breast cancer risk.
Hormonal influences significantly affect breast cancer risk as well. Women who experience an early onset of menstruation or late menopause are at greater risk due to prolonged exposure to estrogen. Furthermore, hormone replacement therapies, especially combination therapies, have been shown to increase breast cancer likelihood.
Despite common myths, it is crucial to clarify that breast cancer can affect anyone, and factors like wearing underwire bras or storing cosmetics in non-glass containers have no scientific backing as causes. Comprehensive research continues to enhance our understanding of breast cancer, and dispelling these myths is essential for informed awareness.
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
One of the most common indicators is the presence of a lump in the breast or underarm area. These lumps may feel different from surrounding tissue and are often painless, although some individuals may experience discomfort. It is crucial to remember that not all lumps are cancerous; however, any noticeable change should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Changes in the size or shape of the breast can signify breast cancer as well. This could include noticeable asymmetry or alterations in the contour of the breast. Women may also observe changes in the texture or appearance of the skin over the breast, such as dimpling or a sudden increase in redness or swelling. These skin changes can accompany underlying malignancies that need further investigation.
Another significant symptom is the presence of discharge from the nipple, which can occur even when not breastfeeding. This discharge may be clear, bloody, or a different color, and it can be indicative of various medical conditions, including breast cancer. It’s essential for individuals to be aware of these changes and seek appropriate medical guidance.
Early detection remains crucial in the fight against breast cancer. Regular self-examinations and mammograms are effective means of identifying potential abnormalities before they develop into more serious issues. Awareness of the typical symptoms can empower individuals to take proactive measures in their health journey. By recognizing these signs early and consulting with healthcare providers promptly, there is a better chance of achieving successful treatment outcomes.
Precautions and Preventative Measures
Taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer is essential for individuals, particularly those with a family history of the disease. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is a fundamental approach. Nutrition plays a pivotal role; a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can significantly promote better health. It is advisable to limit the intake of saturated fats, processed foods, and added sugars, which can contribute to weight gain and other health complications.
Regular physical activity is another crucial component of breast cancer prevention. Engaging in exercise for at least 150 minutes per week, whether it be brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can help maintain a healthy weight and improve overall well-being. Furthermore, individuals should strive to limit their alcohol consumption; studies indicate that even moderate drinking may elevate breast cancer risk. Therefore, restricting alcohol to no more than one drink per day for women can be beneficial.
Avoiding tobacco use is critical in reducing cancer risk, as smoking has been linked to various cancers, including breast cancer. Individuals are encouraged to seek help in quitting if needed, utilizing available resources, such as support groups or smoking cessation programs.
Routine medical check-ups are vital. Regular screenings such as mammograms can lead to early detection, which is crucial for successful treatment outcomes. Additionally, individuals with a family history of breast cancer may benefit from genetic screening to determine their risk level and to make informed decisions regarding preventive measures.
Lastly, engaging in awareness campaigns not only fosters personal knowledge but also enhances community understanding. By participating in education initiatives, individuals can promote a broader dialogue, encouraging others to take preventive measures and seek regular screenings.
Can you guess what I’m craving right now? – https://rb.gy/es66fc?Mive
Who is ?